Language Server Support
Many text editors come equipped with "Intellisense" features such as error reporting, smart autocompletion, formatting, and linting—thanks to a language server client. The Language Server Protocol (LSP), developed by Microsoft, enables the creation of tools that operate independently from editors, in contrast to traditional IDEs where tools are tightly integrated.
While Pragtical does not include a built-in language server client, you can access this functionality through the LSP plugin. In this article, we will guide you through the process of setting up language servers for use with the plugin.
Installation
The LSP plugin can be installed like any other plugin.
The LSP plugin optionally depends on lint+ for inline diagnostics and lsp_snippets for autocompletion snippets support. When installing the plugin manually, you may also install these plugins as well.
- ppm
- Miq
- Manual Installation
To install PPM via the command line, run:
$ ppm plugin install lsp
# or
$ pragtical pm plugin install lsp
To install LSP via Miq, add pragtical/lsp into your config.plugins.miq.plugins:
local config = require "core.config"
config.plugins.miq.plugins = {
-- this allows Miq to manage itself
'TorchedSammy/Miq',
-- install lsp
'pragtical/lsp',
}
Afterwards, run the command miq:install to begin installation.
To install the LSP plugin manually, run these commands:
$ cd ~/.config/pragtical/
$ git clone https://github.com/pragtical/lsp plugins/lsp
$ git clone https://github.com/liquidev/lintplus plugins/lintplus
$ wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/vqns/lite-xl-snippets/main/snippets.lua \
-O plugins/snippets.lua
$ wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/vqns/lite-xl-snippets/main/lsp_snippets.lua \
-O plugins/lsp_snippets.lua
They install the plugin with all its dependencies.
Installing Language Servers
The LSP plugin requires language servers to be installed on the system to function.
Some editors such as Visual Studio Code and Neovim tends to have this process
abstracted by plugins. Luckily, some commonly-used language servers are provided
as plugins as well, prefixed with lsp_.
| Plugin | Language(s) | Server | Platforms |
|---|---|---|---|
| lsp_c | C, C++, Objective-C | clangd | Linux, macOS, Windows |
| lsp_lua | Lua | LuaLS | Linux, macOS, Windows |
| lsp_python | Python | Pyright | Linux, macOS, Windows |
| lsp_quicklintjs | JavaScript | quick-lint-js | Linux, macOS, Windows |
| lsp_rust | Rust | rust-analyzer | Linux, macOS, Windows |
| lsp_tex | TeX | texlab | Linux, macOS, Windows |
| lsp_zig | Zig | zls | Linux, macOS, Windows |
Manual Installation
The LSP plugin expects language servers to be accessible in PATH. If you have
installed the language server from package managers such as npm and pip,
please ensure that their local installation directory is in PATH.
Extra attention is required for users of Node.js version managers like nvm, as the npm prefix can change when switching between Node.js versions. Always ensure you launch Pragtical after sourcing nvm. This applies to all of Pragtical's desktop entries as well.
Set Up
If you installed the language servers via plugins, then you should skip this step.
The LSP plugin offers default configurations for most language servers
(inspired by nvim-lspconfig). You can access these configurations by requiring
plugins.lsp.config in your user module. For instance, to configure the
typescript-language-server, you can do the following:
local lspconfig = require "plugins.lsp.config"
-- set up typescript-language-server with default configuration (enough for most people)
lspconfig.tsserver.setup()
-- override the default configuration
lspconfig.tsserver.setup {
verbose = false
}
Features
Once you have configured your language server, you should see a log message
formatted as [LSP] starting (language server name), followed by
[(language server name)] Initialized when you open a file supported by that
language server. These messages confirm that the language server is correctly
set up and actively running for the document.
Enhanced Autocomplete
One of the most prominent features of a language server is to provide autocomplete suggestions. The LSP plugin integrates with the autocomplete plugin to provide this functionality.
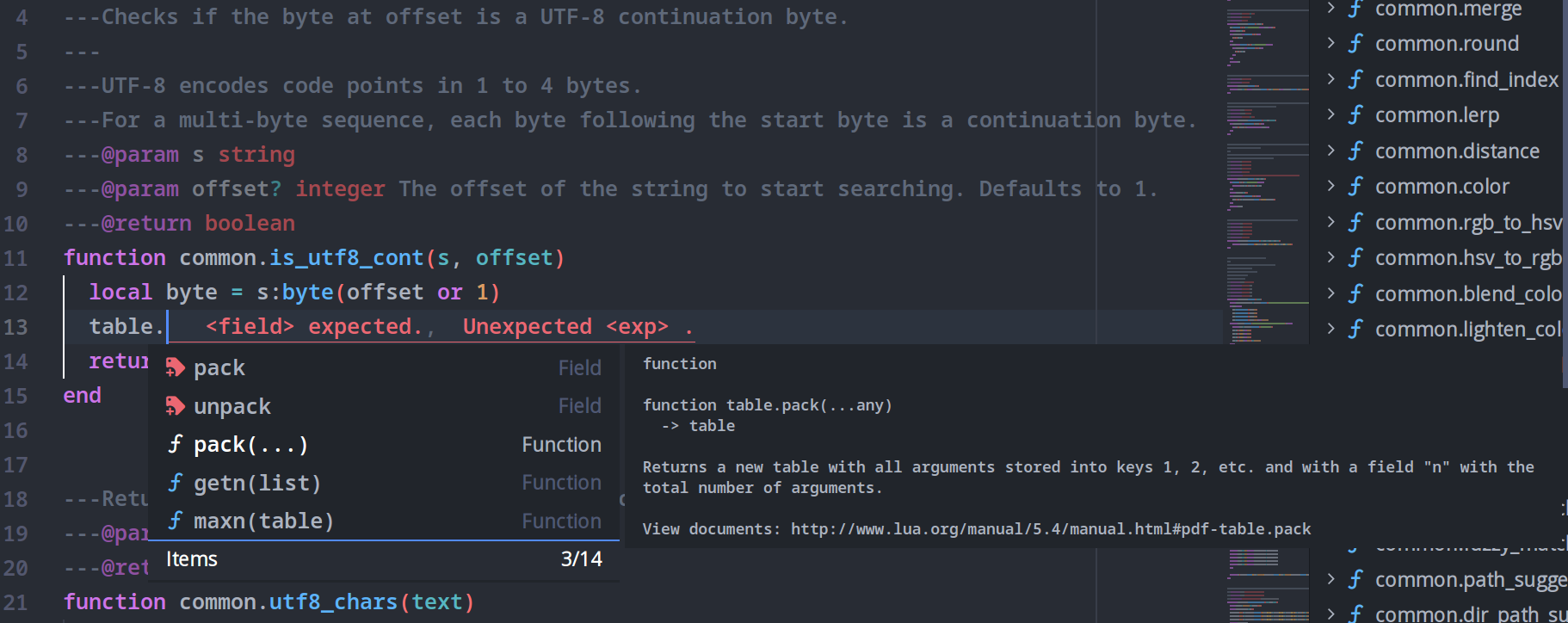
Symbols Tree
A handy feature of the LSP plugin is the symbols tree, which allows for quick navigation within a file while reducing the cognitive load needed to comprehend the structure of the source code.
Snippets
When installed with lsp_snippets, the LSP plugin is able to provide snippets from language servers. The snippets are also integrated with the autocomplete plugin.
Inline Diagnostics
When installed with lint+, the LSP plugin will show diagnostics on the
affected lines. You can disable this with lsp:toggle-diagnostics
(shift+alt+e).
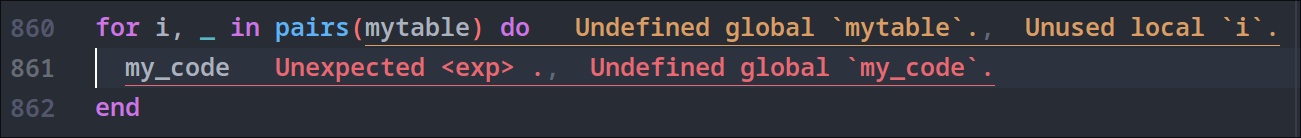
Symbol Search
To view all symbols in a file, you can use lsp:view-document-symbols
(alt+s). You can use lsp:find-workspace-symbol
(shift+alt+s) to find a symbol in the current workspace.
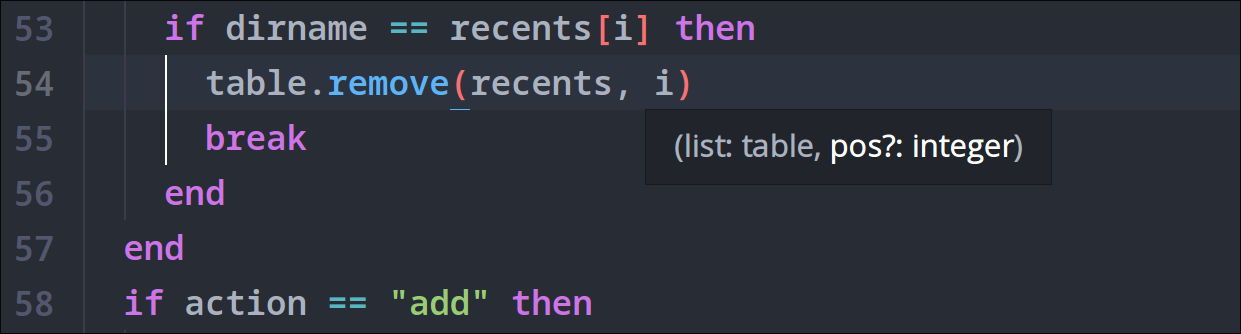
Tooltips
You can hover on symbols to check their types and descriptions.
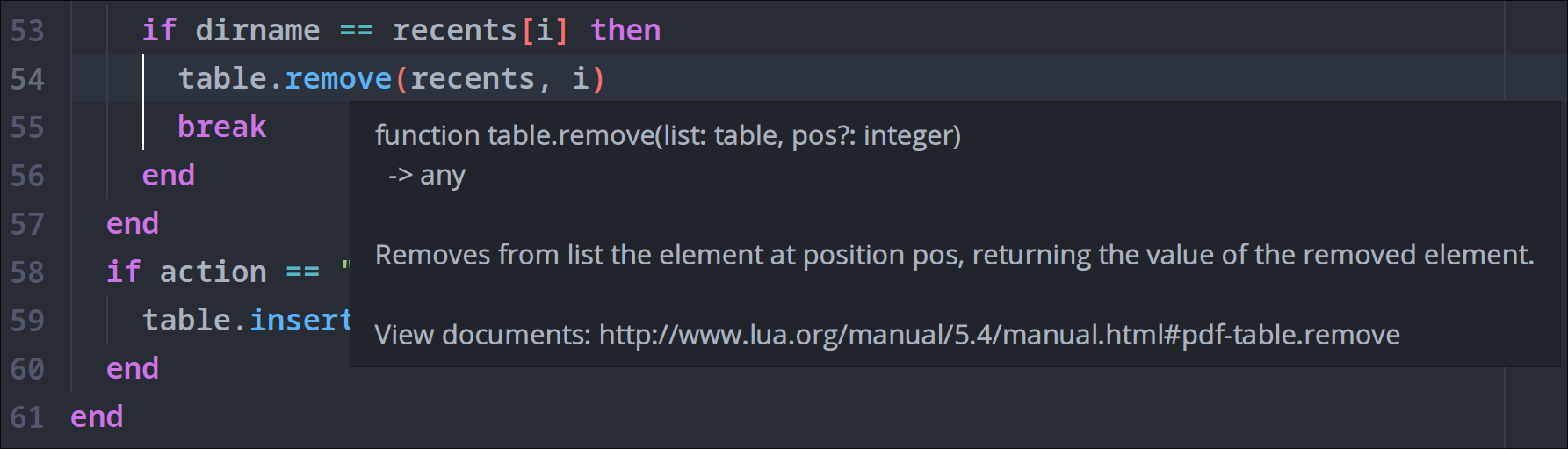
Tooltips will also appear when entering function arguments.
Symbol Renaming
Select the symbol to refactor, press alt+r to enter new name, confirm changes and apply.
Go to Definition
Press alt+d to jump to definition.
Find References
Press alt+f to find references to a symbol.
Document Formatting
Press alt+shift+f to format the current document.
Diagnostics
Press alt+e to view diagnostics messages for the current document. Press ctrl+alt+e to view diagnostics messages for the workspace.
Troubleshooting
We are constantly updating the LSP plugin to fix bugs, add features and improve performance. If you encounter any issues, you should always update to the latest version before trying other steps.
Enable Debug Logging
If you encounter an error message such as
[LSP] (language server name) was shutdown, revise your configuration,
you should try to enable debug logging to see what is happening when the
language server is run.
This is very useful on Windows as the plugin runs the language server with
cmd.exe (to work around wrappers like those provided by npm) and this can
cause errors to never propagate back to the plugin.
- User Module
- Settings UI
In your user module, add:
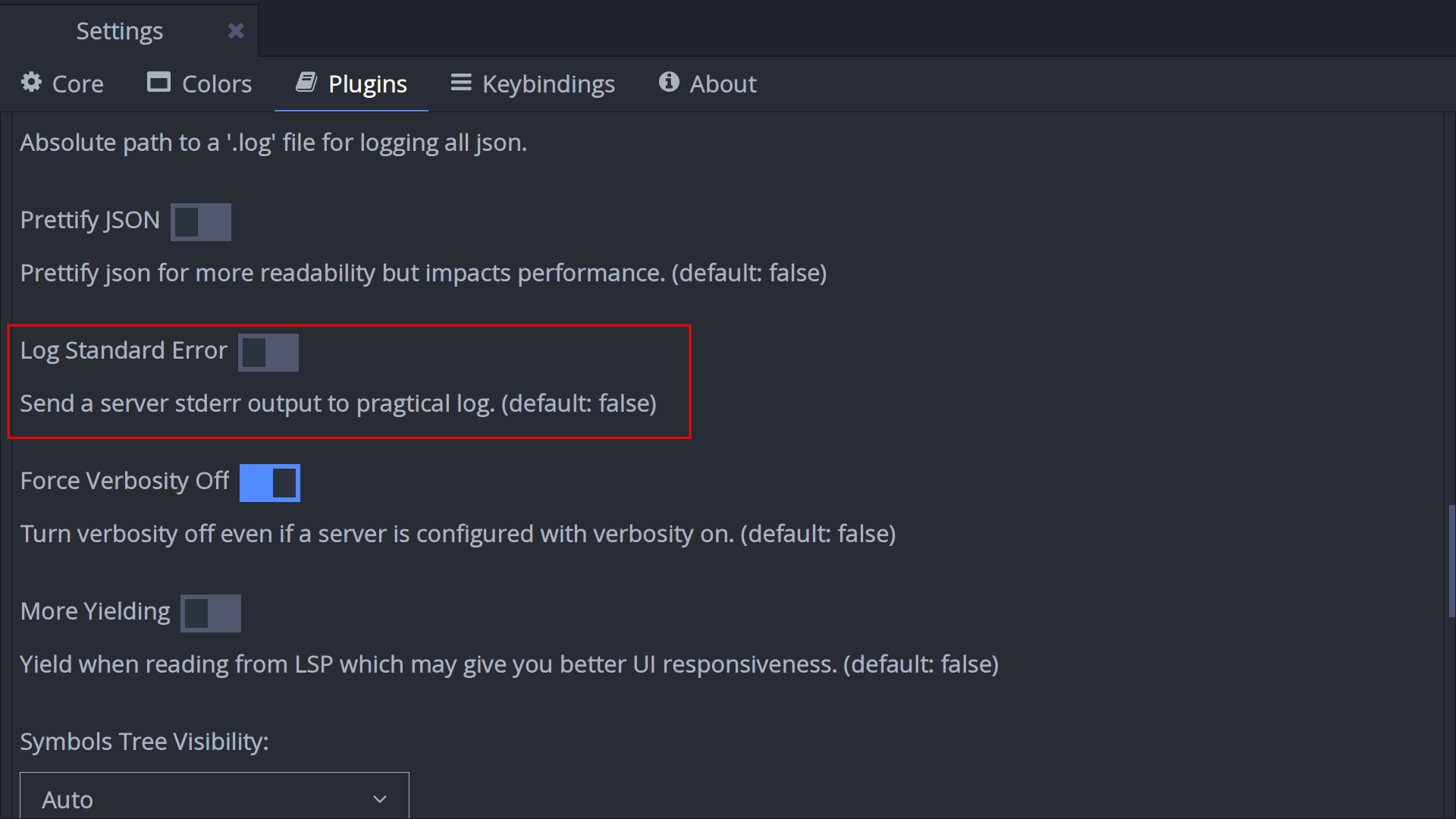
config.plugins.lsp.log_server_stderr = true
Navigate to the "Plugins" tab. Under the "Language Server Protocol" section, enable "Log Standard Error".
Language Servers not starting
There are many reasons why a language server will not launch, the most common
being the plugin cannot find the language server in PATH.
On Windows, this often manifests as
(language server name) is not recognized as an internal or external command, operable program or batch file..
The LSP plugin uses cmd.exe on Windows to launch the language server in order
to work around different file extensions such as .cmd, .bat and .exe.
To solve this issue, make sure that the language server is on PATH.
For non-native language servers (e.g. typescript-language-server), make sure
their installation path with respect to the package managers are on PATH as
well. For npm, this is usually AppData\Roaming\npm on Windows.
jdt.ls launches Microsoft Store
If you've installed jdt.ls from their website, you might run into issues where Microsoft Store is launched instead of running the language server properly.
jdt.ls seems to expect users to have Python installed, and Windows has app
execution aliases built in to redirect python.exe and python3.exe to
Microsoft Store.
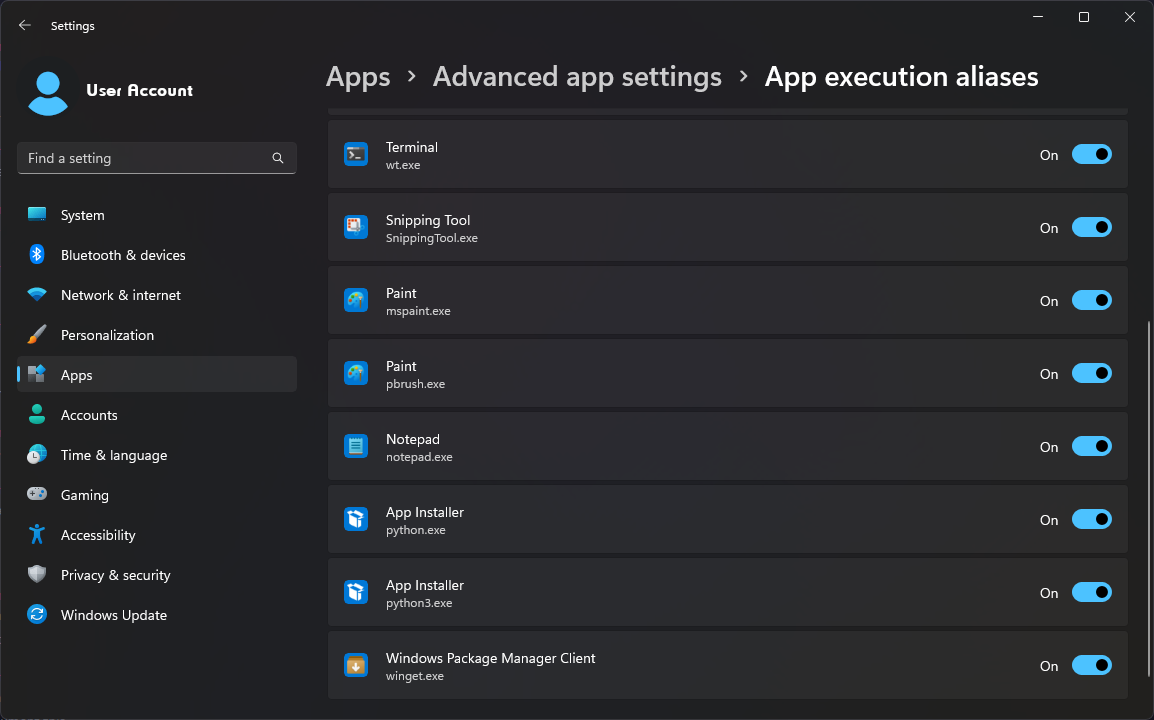
To fix this, install Python. Alternatively, you can follow the instructions from jdt.ls to run the language server without Python at all.